Overview
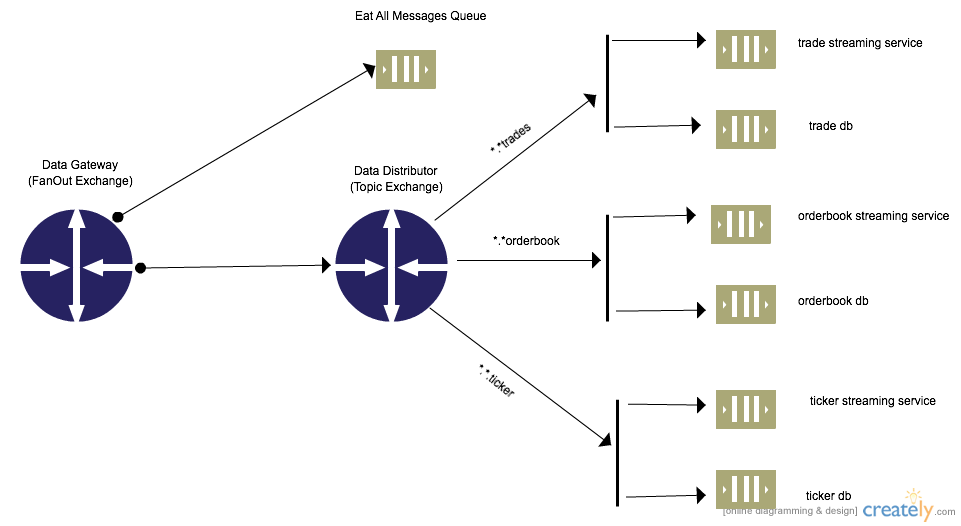
The exchange-exchange binding allows for messages to be sent/routed from one exchange to another exchange. Exchange-exchange binding works more or less the same way as exchange-to-queue binding, the only significant difference from the surface is that both exchanges(source and destination) have to be specified.
Two major advantages of using exchange-exhhange bindings based on experience and what I have found after doing some research are:
- Exchange-to-exchange bindings are much more flexible in terms of the topology that you can design, promotes decoupling & reduce binding churn
- Exchange-to-exchange bindings are said to be very light weight and as a result help to increase performance *
Exchange-To-Exchange Topology
Exchange-To-Exchange Topology Example [Python]
Setup Exchanges & Queues
Send Messages
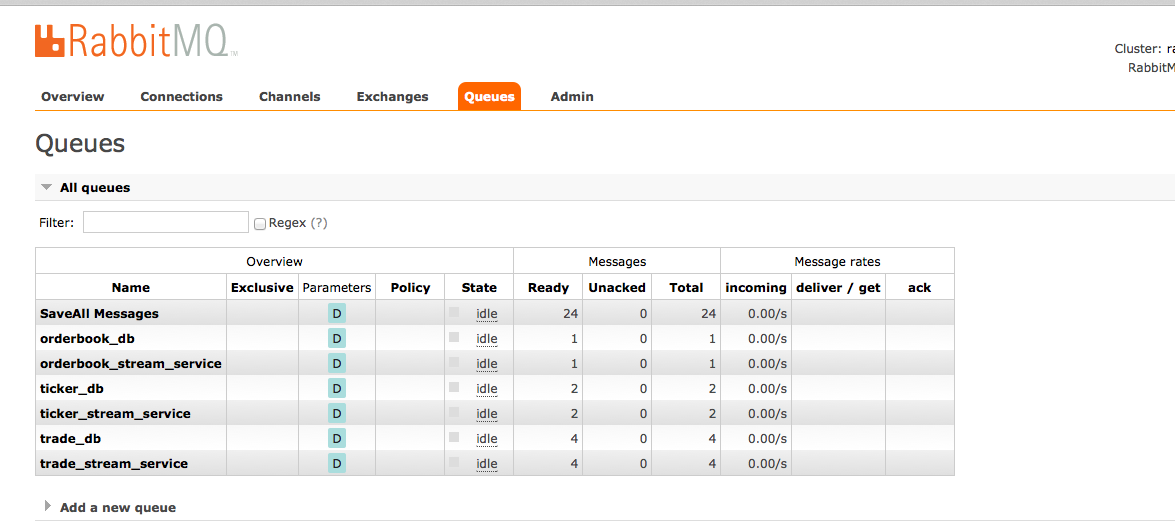
Test sending messages to check that they are being routed to the correct exchanges and queues
[syntax type=”bash”] python send_message_test.py “test.tes.ticker” “lots of tick tock data”[/syntax]
RabbitMq Management Screenshot
* I have not tested the performance of exchange-to-queue and exchange-to-exhcnage myself
*Routing Topologies for Performance and Scalability with RabbitMQ